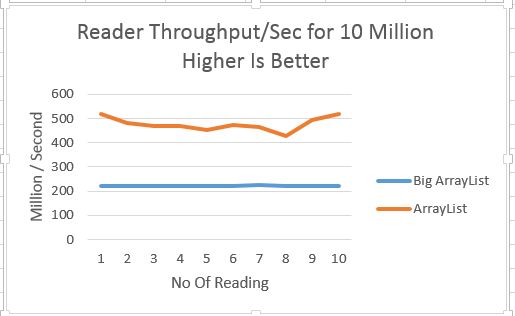
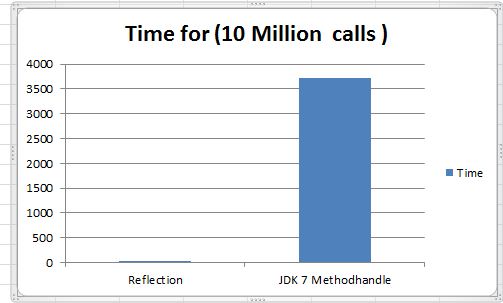
Bit fiddling looks like magic, it allows to do so many things in very efficient way.
In this post i will share some of the real world example where bit operation can be used to gain good performance.

Bit wise operation bootcamp
Bit operator include.
- AND ( &)
- OR ( | )
- Not ( ~)
- XOR( ^)
- Shifts ( <<, >>)
Wikipedia has good high level overview of Bitwise_operation. While preparing for this post i wrote learning test and it is available learningtest github project. Learning test is good way to explore anything before you start deep dive. I plan to write detail post on Learning Test later.
In these examples i will be using below bits tricks as building block for solving more complex problem.
Code for these function is available @ Bits.java on github and unit test is available @ BitsTest.java
Lets look at some real world problems now.
Customer daily active tracking
E-commerce company keep important metrics like which days customer was active or did some business. This metrics becomes very important for building models that can be used to improve customer engagement. Such type of metrics is also useful for fraud or risk related usecase.
Investment banks also use such metrics for Stocks/Currency for building trading models etc.
Using simple bit manipulation tricks 30 days of data can be packed in only 4 bytes, so to store whole year of info only 48 bytes are required.
Code snippet
Apart from compact storage this pattern have good data locality because whole thing can be read by processor using single load operation.
Transmission errors
This is another area where bit manipulation shines. Think you are building distributed storage block management software or building some file transfer service, one of the thing required for such service is to make sure transfer was done properly and no data was lost during transmission. This can be done using bit parity(odd or even) technique, it involves keeping number of '1' bits to odd or even.
Another way to do such type of verification is Hamming_distance. Code snippet for hamming distance for integer values.
Very useful way to keep data integrity with no extra overhead.
Locks
Lets get into concurrency now. Locks are generally not good for performance but some time we have to use it. Many lock implementation are very heavy weight and also hard to share between programs .In this example we will try to build lock and this will be memory efficient lock, 32 locks can be managed using single Integer.
Code snippet
This example is using single bit setting trick along with AtomicInteger to make this code threadsafe.
This is very lightweight lock. As this example is related to concurrency so this will have some issues due to false sharing and it is possible to address this by using some of the technique mention in scalable-counters-for-multi-core post.
Fault tolerant disk
Lets get into some serious stuff. Assume we have 2 disk and we want to make keep copy of data so that we can restore data incase one of the disk fails, naive way of doing this is to keep backup copy of every disk, so if you have 1 TB then additional 1 TB is required. Cloud provider like Amazon will be very happy if you use such approach.
Just by using XOR(^) operator we can keep backup for pair of disk on single disk, we get 50% gain.
50% saving on storage expense.
Code snippet testing restore logic.
Disk code is available @ RaidDisk.java
Ring buffer
Ring buffer is very popular data structure when doing async processing , buffering events before writing to slow device. Ring buffer is bounded buffer and that helps in having zero allocation buffer in critical execution path, very good fit for low latency programming.
One of the common operation is finding slot in buffer for write/read and it is done by using Mod(%) operator, mod or divide operator is not good for performance because it stalls execution because CPU has only 1 or 2 ports for processing divide but it has many ports for bit wise operation.
In this example we will use bit wise operator to find mod and it is only possible if mod number is powof2. I think it is one of the trick that everyone should know.
n & (n-1)
If n is power of 2 then 'x & (n-1)' can be used to find mod in single instruction. This is so popular that it is used in many places, JDK hashmap was also using this to find slot in map.
Conclusion
I have just shared at very high level on what is possible with simple bit manipulation techniques.
Bit manipulation enable many innovative ways of solving problem. It is always good to have extra tools in programmer kit and many things are timeless applicable to every programming language.
All the code used in post is available @ bits repo.
In this post i will share some of the real world example where bit operation can be used to gain good performance.
Bit wise operation bootcamp
Bit operator include.
- AND ( &)
- OR ( | )
- Not ( ~)
- XOR( ^)
- Shifts ( <<, >>)
Wikipedia has good high level overview of Bitwise_operation. While preparing for this post i wrote learning test and it is available learningtest github project. Learning test is good way to explore anything before you start deep dive. I plan to write detail post on Learning Test later.
In these examples i will be using below bits tricks as building block for solving more complex problem.
- countBits - Count number of 1 bits in binary
- bitParity - Check bit added to binary code
- set/clear/toggle - Manipulating single bit
- pow2 - Find next power of 2 and using it as mask.
Code for these function is available @ Bits.java on github and unit test is available @ BitsTest.java
Lets look at some real world problems now.
Customer daily active tracking
E-commerce company keep important metrics like which days customer was active or did some business. This metrics becomes very important for building models that can be used to improve customer engagement. Such type of metrics is also useful for fraud or risk related usecase.
Investment banks also use such metrics for Stocks/Currency for building trading models etc.
Using simple bit manipulation tricks 30 days of data can be packed in only 4 bytes, so to store whole year of info only 48 bytes are required.
Code snippet
Apart from compact storage this pattern have good data locality because whole thing can be read by processor using single load operation.
Transmission errors
This is another area where bit manipulation shines. Think you are building distributed storage block management software or building some file transfer service, one of the thing required for such service is to make sure transfer was done properly and no data was lost during transmission. This can be done using bit parity(odd or even) technique, it involves keeping number of '1' bits to odd or even.
Another way to do such type of verification is Hamming_distance. Code snippet for hamming distance for integer values.
Very useful way to keep data integrity with no extra overhead.
Locks
Lets get into concurrency now. Locks are generally not good for performance but some time we have to use it. Many lock implementation are very heavy weight and also hard to share between programs .In this example we will try to build lock and this will be memory efficient lock, 32 locks can be managed using single Integer.
Code snippet
This example is using single bit setting trick along with AtomicInteger to make this code threadsafe.
This is very lightweight lock. As this example is related to concurrency so this will have some issues due to false sharing and it is possible to address this by using some of the technique mention in scalable-counters-for-multi-core post.
Fault tolerant disk
Lets get into some serious stuff. Assume we have 2 disk and we want to make keep copy of data so that we can restore data incase one of the disk fails, naive way of doing this is to keep backup copy of every disk, so if you have 1 TB then additional 1 TB is required. Cloud provider like Amazon will be very happy if you use such approach.
Just by using XOR(^) operator we can keep backup for pair of disk on single disk, we get 50% gain.
50% saving on storage expense.
Code snippet testing restore logic.
Disk code is available @ RaidDisk.java
Ring buffer
Ring buffer is very popular data structure when doing async processing , buffering events before writing to slow device. Ring buffer is bounded buffer and that helps in having zero allocation buffer in critical execution path, very good fit for low latency programming.
One of the common operation is finding slot in buffer for write/read and it is done by using Mod(%) operator, mod or divide operator is not good for performance because it stalls execution because CPU has only 1 or 2 ports for processing divide but it has many ports for bit wise operation.
In this example we will use bit wise operator to find mod and it is only possible if mod number is powof2. I think it is one of the trick that everyone should know.
n & (n-1)
If n is power of 2 then 'x & (n-1)' can be used to find mod in single instruction. This is so popular that it is used in many places, JDK hashmap was also using this to find slot in map.
Conclusion
I have just shared at very high level on what is possible with simple bit manipulation techniques.
Bit manipulation enable many innovative ways of solving problem. It is always good to have extra tools in programmer kit and many things are timeless applicable to every programming language.
All the code used in post is available @ bits repo.